About this course:
The purpose of this course is to provide education about the nuances and complexities of weaning patients from ventilatory support and the APRN's role throughout this interdisciplinary process.
Course preview
Ventilator Weaning in the Critical Care Patient for APRNs
The purpose of this course is to provide education about the nuances and complexities of weaning patients from ventilatory support and the APRN's role throughout this interdisciplinary process.
By the completion of this course, APRNs will be able to:
- Identify criteria for the patient requiring an advanced airway and ventilator support and describe different ventilator settings and their roles in specific goals of care for the patient.
- Describe the purpose of medications used for the ventilated patient, including paralytics and sedatives.
- Identify weaning criteria for patients and demonstrate an understanding of when it is appropriate for the care team to adjust ventilator settings.
- Identify barriers to extubating patients with a complex course of intubation/advanced airway.
- Interpret lab values relevant to ventilator weaning and describe the steps toward successful discontinuation of mechanical ventilation.
- Describe the role of the APRN in the interdisciplinary process of weaning patients from mechanical ventilation.
The critical care patient may face a vast array of complexities during hospitalization, including traumatic injury, surgery, organ dysfunction, altered laboratory values, sepsis, and others, any of which could contribute to the need for an advanced airway and ventilatory support. The ventilator weaning process involves adjusting ventilator settings to decrease support and allow patients to take on more work of breathing (Epstein & Walkey, 2024). The complex nature of ventilator weaning presents many challenges and comprises a significant portion of the intensive care unit (ICU) workload. Weaning is critical to improved patient outcomes, as prolonged ventilation can lead to complications such as ventilator-associated pneumonia, airway trauma, ventilator-induced lung injury, aspiration, and respiratory muscle weakness (Hyzy, 2023). Patients who are weaned safely and effectively experience less morbidity and mortality than patients requiring prolonged mechanical ventilation (PMV). For these reasons, weaning a patient from the ventilator can and should be considered and discussed throughout their time on mechanical ventilation (MV; Epstein & Walkey, 2024).
Definitions
The following definitions are essential to understanding concepts pertaining to the critically ill and ventilated patient. These definitions cover the course of MV from start to finish.
- Endotracheal intubation involves inserting a breathing tube into the trachea through the vocal cords, allowing secure airway access and oxygen delivery for MV (Amhed & Boyer, 2023).
- Expiration is the process of decreasing lung volume (Lei, 2017). Expiration occurs to expel carbon dioxide (CO2) and prevent it from accumulating in the body (Hallett et al., 2023).
- Extubation is removing an endotracheal tube (ETT) to liberate a patient from ventilator dependence (Hyzy, 2024).
- Hypercapnia, or hypercarbia, is an increased CO2 level in the blood (Lei, 2017).
- Hypoxia is an oxygen (O2) deficiency in the body's tissues (Lei, 2017).
- Inspiration is the process of increasing lung volume (Lei, 2017). Inspiration allows the body to inhale O2 that diffuses across alveolar capillaries to reach arterial blood for delivery to the body's muscles and vital organs (Hallett et al., 2023).
- Noninvasive positive pressure ventilation (NIPPV) is the forced movement of air into and out of the lungs through a face or nasal mask. NIPPV may reduce the need for endotracheal intubation (Brown, 2023).
- Oxygenation is an intervention that provides an increased O2 supply to the lungs and, therefore, to the bloodstream (Mora Carpio & Mora, 2023).
- Respiration transports O2 from atmospheric air to the cells within tissues and CO2 from the cells to the air. This is a three-part process, including gas exchange in the lungs, blood circulation, and gas exchange in the tissues and cells (Lei, 2017).
- A tracheostomy is a surgical procedure that places a breathing tube in the lower neck, allowing secure access to the lower respiratory tract (Hyzy & McSparron, 2024).
- Ventilation is the process of moving air in and out of the lungs, allowing for gas exchange (Mora Carpio & Mora, 2023).
Respiratory Failure
Respiratory failure necessitating ventilator support may occur rapidly or be progressive over time, often related to a chronic illness such as emphysema or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD; Lei, 2017). APRNs should remain attentive to signs of respiratory failure in all patients. The patient's history and baseline respiratory function should be assessed, and in patients with underlying respiratory disorders, it is crucial to evaluate respiratory status frequently (Brown, 2023). Frequent assessment allows the recognition of changes in the patient's status that may prompt early intervention. Manifestations of respiratory failure may include, but are not limited to, tachypnea, tachycardia, cyanosis, sweating, grunting, nose flaring, and decreased oxygen saturation (the amount of oxygen-saturated hemoglobin in the blood relative to total hemoglobin, as measured by pulse oximetry [SPO2] reading; Lei, 2017). In the context of respiratory distress, a patient with hypoxia may present with restlessness or agitation. Worsening hypoxia manifestations may progress to confusion, somnolence, and bradycardia. The patient experiencing chronic CO2 retention may adapt to these changes over time, but acute retention is often first marked by altered mental status, confusion, and somnolence (Brown, 2023).
Intubation and Advanced Airways
The lungs play a critical role in maintaining adequate ventilation by delivering the appropriate tidal volume (TV) to maintain acceptable O2 and CO2 levels in the blood. The brain's respiratory center regulates the rate and depth of breathing to keep these components in balance. In cases of illness, the body may require support via MV (Hallet et al., 2023). MV requires access to the patient's airway, which can be accomplished by inserting a breathing tube. In the setting of acute respiratory failure, an ETT may be placed through the mouth, or sometimes the nose, into the trachea. The decision to intubate should be made when a thorough patient assessment indicates that MV is necessary for their safety. Brown (2023) recommends a three-question approach as outlined below.
- Is there a failure of airway maintenance or protection?
- If yes, intubate.
- If no, move to the next question.
- Is there a failure of oxygenation or ventilation?
- If no, move to the next question.
- If yes, evaluate the patient for NIPPV.
- If not a NIPPV candidate, intubate.
- If a candidate, attempt NIPPV. If unsuccessful, intubate.
- Does the anticipated clinical course require intubation?
- If yes, intubate.
- If no, continue to observe.
Regular assessments should evaluate the patient's ability to protect their airway and manage secretions and airway patency. Airway protection is the ability to guard against aspiration while breathing, which requires a sufficient level of consciousness (Glasgow Coma Scale [GC
...purchase below to continue the course
Even though well-planned algorithms and outlines are available in the decision-making process of intubation, nothing replaces patient assessment and clinical judgment. There are outlying circumstances that may not fit into the three-question algorithm where a patient is safer with a secured airway despite no apparent manifestations of respiratory distress. For example, one may anticipate fluid resuscitation in a patient with sepsis with underlying respiratory disease and recognize that pulmonary edema could be a consequence of this treatment. The team should use clinical judgment to determine if an advanced airway's security is preemptively indicated to avoid the possibility of potential emergency intubation in the future (Brown, 2023).
In most ICU and emergency department patients requiring advanced airways, rapid-sequence intubation (RSI) is suitable. This intubation method is used in patients at risk for aspiration (e.g., those who have not fasted) or at risk of losing a secure airway. If RSI becomes necessary, at least one functioning intravenous (IV) line should be in place, along with monitoring equipment for telemetry, blood pressure, pulse oximetry, and capnography. All necessary airway and resuscitation equipment and personnel should be readily available (Brown & Sakles, 2023). An induction agent is administered to sedate the patient initially, such as propofol (Diprivan) or etomidate (Amidate; Bittner, 2023). Etomidate (Amidate) has been shown to produce rapid loss of consciousness with a relatively stable safety profile (negligible effect on heart rate or blood pressure, yet a favorable reduction in cerebral blood flow and ICP), thus making it a frequent choice in emergency, ICU, and pre-hospital situations. It is typically dosed at 0.2 to 0.3 mg/kg for this purpose. It is a potent steroid inhibitor, potentially causing temporary adrenal insufficiency of unknown clinical significance. It may also cause myoclonic movements, nausea, vomiting, and trismus (painful muscle spasms that limit the ability to open the jaw). Ketamine (Ketalar) dosed at 2 mg/kg may also be used for this purpose, although it is contraindicated in patients with significant coronary artery disease or non-traumatic compromise of intracranial and cerebrovascular dynamics (Flynn & Shehabi, 2012).
After this, a neuromuscular blocking agent (NMBA), or paralytic, should be used. The two NMBAs most commonly used for induction purposes are succinylcholine (Anectine) and rocuronium (Zemuron). Succinylcholine (Anectine) is the only depolarizing NMBA approved for use in the U.S. It functions by binding to acetylcholine receptors on the motor neuron endplate, first causing depolarization followed by blocking neuromuscular transmission. For intubation, succinylcholine (Anectine) is typically dosed at 0.60 to 1.5 mg/kg with an ultrashort duration (half-life of less than one minute and 5 to 10 minutes to 25% recovery). It presents a higher risk for hyperkalemia in critically ill patients and is used almost exclusively for intubation purposes or severe laryngospasm. It may also cause myalgia and bradycardia. It is contraindicated in patients with hyperkalemia, malignant hyperthermia, muscular dystrophy, and pseudocholinesterase deficiency, and it is not recommended for use in children (Bittner, 2023). Additional conditions that may contraindicate the use of NMBAs include cerebral palsy, hemiplegia, peripheral nerve injury, or severe chronic botulism or tetani (Clar, 2023).
Nondepolarizing agents include benzylisoquinolinium compounds, such as cisatracurium (Nimbex), and aminosteroid compounds, such as rocuronium (Zemuron). Both function by binding to acetylcholine (ACh) receptors and preventing endplate potentials. Rocuronium (Zemuron) has both a rapid onset of action (1 to 2 minutes) and intermediate duration (30 to 80 minutes to 25% recovery). Typical intubation dosing for rocuronium (Zemuron) is 0.45 to 0.90 mg/kg, cisatracurium (Nimbex) is 0.1 to 0.15 mg/kg (within 2 minutes of intubation), and vecuronium (Norcuron) is 0.08 to 0.12 mg/kg (Clar, 2021). RSI may justify a single dose of rocuronium (Zemuron) of up to 1.2 mg/kg or a single dose of cisatracurium (Nimbex) or vecuronium (Norcuron) of up to 0.2 mg/kg. The onsets of cisatracurium (Nimbex) and vecuronium (Norcuron) are slightly slower, at 4 to 6 minutes and 3 to 4 minutes, respectively. Those with severe septic shock may require higher dosing of cisatracurium (Nimbex), although this is the preferred agent in patients with renal or hepatic insufficiency. Vecuronium (Norcuron) and rocuronium (Zemuron) should be avoided in patients with hepatic or renal insufficiency if possible (Bittner, 2023).
In emergency intubations, esophageal intubation can occur in up to 1 in 18 intubations. The APRN should be familiar with the standards for verifying ETT placement. While auscultation of bilateral breath sounds is important, the most reliable standard of care for verifying ETT positioning is waveform capnography. With no waveform, it is likely that the ETT is placed in the esophagus instead of the trachea and needs to be replaced. In circumstances without wave capnography monitoring capability, a color-changing capnography device may be used. A qualified provider may even confirm placement with ultrasound until a chest x-ray can be taken for final confirmation (Chrimes et al., 2022).
If prolonged ventilator support is anticipated (usually greater than 10 days) or when ventilator weaning is unsuccessful, a tracheostomy tube may be applicable for a patient requiring ventilator support. The placement of a tracheostomy tube has been shown to reduce the work of breathing, airway resistance, peak inspiratory pressures, and intrinsic or auto-PEEP (positive end-expiratory pressure). These changes typically make weaning from MV easier for patients and reduce the need for sedation. When a tracheostomy is placed, the head and face are no longer encumbered by invasive equipment, immediately enhancing patient comfort. Specialized tubes also allow patients with tracheostomies more ability to communicate verbally, reducing patient anxiety. Disadvantages include the potential for cuff-site and stoma complications, increased risk for tracheal injury, site infections, and inadvertent decannulation. Tracheostomy procedures may be performed surgically or percutaneously, allowing the procedure to be completed at the bedside. It may be done with ultrasound guidance, bronchoscopy guidance, or dilatational. Percutaneous dilatational tracheostomies have demonstrated lower infection rates and may decrease the risk of major bleeding and mortality. Surgically placed tracheostomy tubes are easier to replace if inadvertently dislodged, as dilated stomas tend to recoil faster than surgically created tracts. Dislodged tracheostomy tubes can be replaced with a new tube, but if decannulation occurs within the first 10 days, the patient may need to be orally intubated to avoid generating a false tract. The site can then be revised in a controlled environment. These complications can be prevented with the proper use of trach ties and stay sutures in appropriate circumstances (Hyzy & McSparron, 2024).
Monitoring and Assessing the Critically Ill Patient
The acute care APRN is responsible for monitoring ventilated patients according to unit protocol, which typically requires frequent vital signs, including heart rate (HR) and rhythm, respiratory rate (RR), SPO2, blood pressure (BP), and temperature. Some units may require end-tidal CO2 monitoring (ETCO2), a measurement of CO2 during expiration taken from the ETT, or other advanced hemodynamic monitoring. APRNs should be trained to be familiar with the capabilities of monitoring systems and parameters applicable to patient conditions and adjust alarm settings accordingly (Lewandoska et al., 2020).
The APRN should collaborate with the respiratory therapist to ensure applicable ventilator alarms and safety protocols are in place. "False alarms" can decrease staff responsiveness, so alarm settings should be tailored to decrease their frequency. Properly set alarm parameters reduce the risk of missing a real alarm in a life-threatening circumstance (Poncette et al., 2020). The patient's RR, SPO2, and ETCO2 relate directly to ventilator settings and should be monitored closely. However, SPO2 may prove unreliable in a patient with poor peripheral perfusion (Brown, 2023).
Arterial Blood Gas
The interprofessional team may also evaluate lab values, including arterial blood gas (ABG). When interpreted correctly, ABG is a helpful tool for assessing respiratory failure and the patient's ventilator settings (Castro et al., 2024). They may be used as a component of the clinical decision-making regarding the need to intubate, as an assessment tool throughout intubation, and during ventilator weaning (Epstein, 2024b). ABG values measure several components related to respiratory function. Relevant measurements, as quantified and defined by Castro and colleagues (2024), include the following:
- pH - measured acid-base balance of the blood (reference range 7.35 to 7.45)
- PaO2 - measured partial pressure of oxygen in arterial blood (reference range 75 to 100 mm Hg)
- PaCO2 - measured partial pressure of carbon dioxide in arterial blood (reference range 35 to 45 mm Hg)
- HCO3 - calculated concentration of bicarbonate in arterial blood (reference range 22 to 26 mEq/L)
- SaO2 - calculated oxygen saturation of arterial blood (reference range 95% to 100%)
CO2 is an acid regulated by the respiratory system, while bicarbonate (HCO3) is a base controlled by the metabolic system, primarily the kidneys. When interpreting ABG values, the APRN should first observe the pH. A pH below 7.35 is acidotic, while anything above 7.45 constitutes alkalosis (Theodore, 2023). Further interpretation is required to determine if an irregularity in pH value is related to respiratory or metabolic failure or if an expected pH value is due to compensation. The APRN should evaluate the PaCO2 (acid) and HCO3 (base) values to discern the imbalance's origin. Elevated PaCO2 indicates hypoventilation or retention of CO2, while decreased levels reflect hyperventilation or excessive release of CO2. The APRN must also analyze HCO3 levels to determine if the patient's imbalance is metabolic or respiratory in origin (Castro et al., 2024). In most cases, a low pH with a high PaCO2 indicates respiratory acidosis. However, a low pH with a low PaCO2 suggests that there is a metabolic force driving the imbalance (Emmet & Palmer, 2022).
Blood gasses may also reflect a mixed acid/base disorder, where PaCO2 and HCO3 are altered. The origin of mixed disorders is more difficult to identify, so assessing the patient's health history and current status is essential. For example, a patient with chronic renal failure may present with metabolic acidosis (i.e., decreased HCO3) due to the inability to excrete acids in the urine. If they hyperventilate due to anxiety, they will blow off excessive CO2 and present with a low PaCO2. The combined low HCO3 and CO2 may result in a pH that is within normal limits due to compensation. Mixed respiratory-metabolic disorders typically cause abnormal PaCO2 or HCO3 values accompanied by a normal pH (Achanti & Szerlip, 2023). Compensatory responses rely on the lungs and kidneys functioning properly and vary based on the severity of the pH disturbance that initiates this response. Respiratory compensation occurs significantly faster than the compensatory metabolic response from the kidneys. Initiation of the compensatory response can take hours to days (Castro et al., 2024).
ABG interpretation can discern if the patient is experiencing type one (hypoxic) or type two (hypercapnic) respiratory failure. Both conditions will result in a PaO2 below 60 mm Hg. Hypoxic respiratory failure, or lung failure, is identified by a normal or near-normal PaCO2 level. This is usually the result of a condition in which the blood is inadequately oxygenated when passing through the lungs (e.g., an arteriovenous shunt, gas diffusion impairment, or ventilation/perfusion mismatch). Hypercapnic respiratory failure results in a PaCO2 above 50 mm Hg. This may be a consequence of chest trauma, respiratory fatigue, excessive airway resistance, or decreased respiratory drive (Lei, 2017).
Blood gas interpretation is particularly relevant to the ventilated patient as these lab values can inform ventilator setting adjustments. For example, respiratory acidosis implies that the patient is retaining too much CO2. Increasing the ventilator's RR may allow the patient to "blow off" or expel the excess CO2. In contrast, if a patient's ABG values indicate respiratory alkalosis, then reducing the RR could increase the amount of CO2 to improve this imbalance (Allen, 2023). ABG readings provide critical information regarding whether a patient is ready to wean to a lower ventilator setting or be extubated. However, these values should always be considered in conjunction with a thorough patient assessment to ensure factors such as patient response and respiratory effort are appropriate (Epstein & Walkey, 2024).
While ABGs are an informative decision-making tool throughout a patient's hospitalization, the patient's clinical presentation should always be considered. For example, the patient's lab values may fall within expected limits on paper. Still, intervening must be contemplated if a patient is in apparent respiratory distress or at risk for rapid onset of respiratory failure (Brown, 2023).
Case Study 1
The APRN is receiving a change-of-shift report at 1900 regarding a patient who was extubated earlier today. This patient has a history of COPD and type 2 diabetes and was intubated for 4 days. They were extubated at 1500 after a successful 30-minute spontaneous breathing trial. The day shift APRN reports that the patient was alert, oriented, and pleasant after extubation and is now resting comfortably in their room with their eyes closed on 2 liters O2 via nasal cannula. They will be observed overnight and likely transferred to the stepdown unit tomorrow pending their clinical course.
The APRN walks into the patient's room at 1930 to perform an assessment and attempts to wake them to assess their orientation and level of sedation using the Richmond Agitation-Sedation Scale (RASS). The patient does not awaken to verbal or gentle physical stimulation. The APRN checks the monitor and sees that the patient's heart rate is 88/min (expected sinus rhythm), blood pressure is 128/73 mm Hg, respiratory rate is 8/min, and SpO2 is 94%. The APRN performs a sternal rub and speaks loudly to the patient, who briefly opens their eyes without speaking.
The APRN pages their supervising provider and respiratory therapist to the bedside. What interventions should the APRN consider in this situation?
The APRN should consider the causes of the patient’s poor mentation. Since the patient was recently extubated and has a history of COPD, a likely cause is CO2 retention. The APRN should consider ordering NIPPV and have a low threshold for reintubation. An ABG may help to confirm an elevated PaCO2 level.
Understanding Mechanical Ventilation
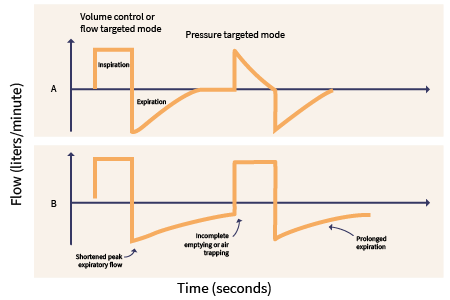
Natural ventilation without intervention occurs as a negative pressure system. The diaphragm pushes down during inspiration, creating pressure in the pleural cavity that pulls air into the airways and lungs. MV operates utilizing positive pressure. The ventilator pushes air into the lungs to open the alveoli, promoting gas exchange and positive pressure in the pleural space (see Figure 1). The primary objectives of MV include relieving respiratory distress, improving pulmonary gas exchange, permitting lung or airway healing, and reversing hypoxemia or hypercapnia (Mora Carpio & Mora, 2023). Goals should include patient comfort, safety, and, ultimately, the patient's liberation from the ventilator (Epstein, 2023). The American Thoracic Society (ATS) and American College of Chest Physicians (ACCP) both advocate for the use of early mobilization with a physical therapist in mechanically ventilated patients; this prevents the associated complications of prolonged immobility and promotes liberation from MV (Epstein, 2024a).
Figure 1
Mechanical Ventilation Waveforms
The following definitions are key components to understanding the concepts of MV (Hallett et al., 2023; Lei, 2017; Mora Carpio & Mora, 2023).
- Ventilation is the exchange of gas between atmospheric air and the lungs, whether by spontaneous breaths or delivered by a ventilator.
- Compliance measures pressure tolerance in the lungs and chest wall, calculated by dividing volume by change in pressure. Standard lung compliance is around 100 mL/cm H20. Decreased lung compliance is common in patients with a respiratory illness that causes lung stiffness, such as acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) or pulmonary fibrosis.
- FiO2, or fraction of inspired oxygen, is the percentage of O2 in the air that is delivered to the patient.
- Flow is the speed at which the ventilator delivers breaths, reported in breaths per minute.
- Minute ventilation is a measurement of the amount of air that enters the lungs per minute - a product of RR multiplied by TV.
- Oxygenation is an intervention that increases the delivery of O2 to the lungs, allowing diffusion into the bloodstream. In MV, this is accomplished through modifications to the FiO2 percentage or PEEP.
- Peak pressure is the pressure achieved during inspiration when that air is being pushed into the lungs. Peak pressure measures airway resistance.
- The plateau pressure is the pressure imposed on the small airways and alveoli during MV. An increase in plateau pressure puts the patient at risk of alveolar rupture.
- PEEP is the positive pressure remaining in the lungs at the end of exhalation. PEEP keeps the alveoli open and promotes gas exchange.
- TV is the amount of air that moves in or out of the lungs with each respiratory cycle. Ventilator settings should be adjusted to deliver TVs large enough to ventilate the patient adequately but not large enough to induce traumatic lung injury. The current standard is to use TVs of 6 mL/kg to protect lungs from trauma. On average, this equates to TVs of around 500 mL in a healthy adult male (average of 83 kg or 183 pounds) and 400 mL in a healthy adult female (average of 67 kg or 147 pounds).
Modes of Ventilation
Ventilator settings can be customized to the patient's condition, and the combinations of settings are innumerable. Hyzy & Jia (2023) provide the following descriptions of ventilator settings frequently used in the ICU to provide baseline MV knowledge.
- Volume-controlled or volume-limited ventilation:
- A set TV is delivered to the patient with every breath.
- Airway pressure may vary with breaths, and minute volume is dictated by the RR accompanying the set TV.
- Pressure-controlled or pressure-limited ventilation:
- TVs vary from breath to breath, but peak airway pressure is constant.
- Pressure-controlled modes are associated with lower peak pressures, improved synchrony with the ventilator, and earlier extubation.
Within these categories, ventilator modes are further categorized as follows (Hyzy & Jia, 2023).
- Controlled mechanical ventilation (CMV):
- Volume-controlled minute ventilation is determined by the RR and TV set by the provider. This is most appropriate for heavily sedated or paralyzed patients, as it does not require any patient work.
- CMV may also be delivered with pressure-limited settings, allowing the minute ventilation to be determined by the set RR in conjunction with the inspiratory pressure level.
- Assist control (AC):
- With a volume-controlled setting (AC/VC), the provider sets the RR and TV, but the patient may trigger additional breaths. The patient receives the same TV with every breath.
- With a pressure-controlled setting (AC/PC), inspired volumes will vary, but peak inspiratory pressures are limited.
- Intermittent mandatory ventilation (IMV):
- The provider sets the minimum RR and TV, but the patient can increase the minute ventilation with spontaneous breaths of whatever volume the patient can generate.
- Synchronized intermittent mandatory ventilation (SIMV):
- The provider sets the minimum RR and TV, and ventilator breaths are synchronized with the patient's inspiratory effort.
- The RR can vary depending on the patient's respiratory drive and initiation of breaths but will not drop below the minimum or mandatory set.
- Pressure support ventilation (PSV):
- The provider sets the inspiratory pressure level, PEEP, and FiO2, but the patient controls the RR and TV.
- PSV is a more "comfortable" mode that gives the patient greater control over inspiratory flow and RR while the machine's pressure augments the patient's spontaneous breath efforts.
- Levels of pressure support can be adjusted based on the patient's condition, and a lower level of pressure support requires the patient to work more to breathe. This makes PSV a useful setting for a patient being weaned from the ventilator since the interprofessional team can observe the patient's respiratory drive and endurance.
Nursing Alert: When a patient is being ventilated with the PSV setting, it is important to ensure they are receiving adequate minute ventilation, since the patient is in control of TV and RR, and these factors may vary. PSV CANNOT provide full ventilatory support. A heavily sedated patient is not a suitable candidate for this setting (Hyzy & Jia, 2023).
- Continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP):
- CPAP is delivered without variation, with no RR or TV set. The patient must initiate all breaths.
Case Study 2
The APRN is caring for a patient who has been intubated for several days with worsening respiratory status. The patient is sedated with propofol (Diprivan) and is receiving CMV from the ventilator, with the FiO2 set to a maximum of 100%. This patient weighs 100 kg, and their TVs are set to 600 mL per lung protective ventilation standards. Their blood oxygenation saturation remains poor despite receiving full O2 support. Since FiO2 cannot be increased beyond 100%, what other adjustment may be made to the ventilator settings to help improve oxygenation?
Considerations: The PEEP setting on the ventilator determines the degree to which alveoli remain open at the end of a breath, allowing for varying degrees of gas exchange. Increasing PEEP may promote increased gas exchange in the alveoli, allowing the patient's bloodstream to absorb more O2 on inspiration.
Sedation
Sedative and analgesic medications are almost universally administered to patients undergoing invasive MV. These medications provide patient comfort and prevent agitation, which can lead to catastrophic consequences in a disoriented patient in the ICU, such as self-extubation or removal of invasive catheters (e.g., central lines or Foley catheters; Temesgen et al., 2021).
Selecting the ideal sedative and analgesic should take a patient's condition into account and be adjusted and reevaluated in response to changes in clinical status. Multiple sedatives and pain medications can be used in combination and titrated to patient-specific goals. While etomidate (Amidate) is frequently used as an induction sedative, it is not used continuously. The most used continuous sedatives include (Fuchs, 2024; Morelli et al., 2019):
- Propofol (Diprivan) can be used for light or deep sedation, depending on the dose administered. It is used frequently due to its short half-life and quick reversal with short-term use. It should be given through a large-bore IV if given peripherally.
- Propofol (Diprivan) may cause hypotension, which can be profound with significant doses. BP should be monitored diligently, especially when infusion rates are changed. Other adverse effects include bradycardia, respiratory depression, decreased myocardial contractility, and injection site pain.
- Propofol (Diprivan) is typically dosed at 5 to 50 mcg/kg/minute. It can be titrated every 5 to 10 minutes, adjusting in 5 to 10 mcg/kg/minute increments. Dosing should not be weight-based in patients with obesity, and the maximum dosage is typically 70 mcg/kg/minute. However, the risk of propofol infusion syndrome (PRIS, characterized by hyperkalemia, metabolic acidosis, renal and cardiac failure) is increased with doses in this range. Routine monitoring of triglycerides, lactate, creatinine kinase, and myoglobin may assist with identifying PRIS. The onset is 1 to 2 minutes, and the duration is 3 to 10 minutes.
- Benzodiazepines, commonly midazolam (Versed), lorazepam (Ativan), or alprazolam (Xanax), have significant historical use and are among the most used sedatives in critical care settings worldwide. However, benzodiazepines for continuous sedation were commonplace before ICU sedation guidelines were widespread, and the push for sedation weaning was not as typical.
- Benzodiazepines are known for unpredictable accumulation, especially when given in higher doses to achieve deep sedation. The consequence of this accumulation is prolonged sedation, even after the infusion has been discontinued. Prolonged use typically leads to tolerance or the need for a higher dose to achieve the same clinical effect (Fuchs, 2024).
- Benzodiazepines may increase delirium risk, ventilator days, and length of ICU stay (Fuchs & Bellamy, 2024).
- Midazolam (Versed) is a potent amnestic associated with respiratory and cardiovascular depression. In rare cases, patients may experience paradoxical effects such as agitation, restlessness, and aggression. It may lead to delirium. Loading doses of midazolam (Versed) range from 0.01 to 0.05 mg/kg (0.5 to 4 mg), and multiple loading doses may be required. Maintenance dosing is typically 0.02 to 0.1 mg/kg/hour (2 to 8 mg/hour) with intermittent dosing as needed. Benzodiazepine dosing should not be weight-based in patients with obesity. Onset is typically 2 to 5 minutes, and duration is 30 minutes. It is hepatically metabolized and may have a prolonged half-life in critically ill patients with renal or hepatic impairment. It may interact with many azole antifungals or antiretrovirals and other medications metabolized by CYP3A4 (Fuchs, 2024).
- Lorazepam (Ativan) has a slower onset, making titration somewhat delayed and more challenging. Common adverse effects include respiratory depression, delirium, and oversedation. The staff should be observant of IV-line precipitate, with an in-line filter in use when available. Loading doses of lorazepam (Ativan) range from 0.02 to 0.04 mg/kg (1 to 2 mg), and multiple loading doses might be required. After this, it can be dosed intermittently at 0.02 to 0.06 mg/kg (1 to 4 mg) every 2 to 6 hours (preferred) or 0.01 to 0.1 mg/kg/hour (0.5 to 10 mg/hour) via continuous infusion. Benzodiazepine dosing should not be weight-based in patients with obesity. Onset is typically 15 to 20 minutes, while the duration may be as long as 6 to 8 hours. Propylene glycol solvent can accumulate with prolonged use or higher dosing, leading to metabolic acidosis. Lorazepam (Ativan) does not interact with medications metabolized by CYP3A4 (Fuchs, 2024).
- Dexmedetomidine (Precedex) is generally used for light to moderate sedation and in patients experiencing agitation and ICU delirium. Dexmedetomidine (Precedex) has been found to prevent and resolve ICU delirium (Reade et al., 2016). It is a central sympatholytic (i.e., alpha2 agonist) with moderate anxiolytic and analgesic properties (Fuchs, 2024).
- Patients receiving dexmedetomidine (Precedex) are more arousable than patients receiving other sedating agents, allowing successful maintenance of light to moderate sedation. This improves the patient's ability to communicate and interact with the care team, even when intubated (Reel & Maani, 2023).
- A study by Reade and colleagues (2016) found that patients treated with dexmedetomidine (Precedex), as compared to midazolam (Versed), developed delirium less often and were liberated from MV sooner.
- Dexmedetomidine (Precedex) produces an analgesic effect and less respiratory depression. Continuous infusions can even be used on non-intubated patients (Reel & Maani, 2023).
- When administering a dexmedetomidine (Precedex) infusion, there is a risk of bradycardia; in some cases, the HR may drop below 40/min. The infusion should be adjusted accordingly if the patient becomes bradycardic, and the provider should be notified to determine if additional intervention is required (Morelli et al., 2019). It can also lead to significant alterations in blood pressure, nausea, and atrial fibrillation (Fuchs, 2024).
- Dexmedetomidine (Precedex) loading doses are optional and rarely used due to the risk of cardiovascular instability; if used, they should be given over 10 minutes and dosed at 1 mcg/kg. Maintenance dosing is typically 0.2 mcg/kg/hour initially and can be titrated up every 30 minutes to a maximum of 1.5 mcg/kg/hour. The onset is typically 15 minutes but can be 5 to 10 minutes when a loading dose is used, with a duration of 1 to 2 hours. These doses should be reduced in renal or hepatic impairment and tapered carefully to avoid withdrawal manifestations (Fuchs, 2024).
Analgesia
Analgesia addresses the pain of patients in the ICU and is often given alone or in conjunction with sedative medications. Untreated pain can lead to agitation, higher energy expenditure, and irregularities in the immune response. It also increases the risk of posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD) if prolonged (Murray et al., 2020). When managing patients who are unable to communicate verbally, a nonverbal pain scale may be used per unit/facility policy to discern the level of pain the patient may be experiencing (Chanques & Gélinas, 2022).
- Fentanyl (Sublimaze) is the analgesic agent most frequently used in the ICU for routine pain management, procedural analgesia, and ICU sedation.
- Fentanyl (Sublimaze) is a short-acting opiate that is less sedating than morphine (Duramorph, Infumorph). It can, however, produce somnolence and sedation in high doses, especially in patients with impaired renal function (Casamento et al., 2021). It typically causes less hypotension than other analgesic agents. It is lipophilic, accumulates in adipose tissue with prolonged use, and can cause chest wall rigidity at higher doses (Fuchs, 2024).
- Fentanyl (Sublimaze) potentiates the effects of sedatives if administered concurrently and should be titrated in conjunction with the accompanying sedative to the patient-specific goal (Casamento et al., 2021).
- Fentanyl (Sublimaze) loading doses are typically 1 to 2 mcg/kg (25 to 100 mcg). Maintenance dosing can be 0.35 to 0.5 mcg/kg (25 to 50 mcg) every 30 to 60 minutes or 0.7 to 3 mcg/kg/hour (50 to 200 mcg/hour) via continuous infusion with as-needed bolus administration. Dosing should not be weight-based in patients with obesity, and the maximum dose should be 10 mcg/kg/hour (700 mcg/hour). The onset of fentanyl (Sublimaze) is 1 to 2 minutes, and its duration is 30 to 60 minutes. It is metabolized hepatically (Fuchs, 2024).
- Morphine (Duramorph, Infumorph) is an opiate administered for pain management in critical care patients and especially for palliation in patients with a terminal illness.
- Morphine (Duramorph, Infumorph) is longer acting than fentanyl (Sublimaze) and has known adverse effects, including hypotension, respiratory depression, and bradycardia. It may also cause myocardial depression and reduced preload (Fuchs, 2024).
- A study by Casamento and colleagues (2021) demonstrated that morphine use for analgesia for patients in the ICU may increase the number of ventilator days in the long run when compared to fentanyl.
- Loading doses of morphine (Duramorph, Infumorph) are typically 2 to 10 mg, while maintenance dosing is either 2 to 4 mg every 1 to 2 hours or a continuous infusion of 2 to 30 mg/hour. The onset is typically within 5 to 10 minutes, while the duration of effect is 4 to 5 hours. It is not metabolized via the CYP3A4 route like fentanyl (Sublimaze) and hydromorphone (Dilaudid). Despite this, dose adjustments are suggested for renal or hepatic impairment (Fuchs, 2024).
- Ketamine may be used for ventilated patients for dissociative anesthetic sedation with some analgesic properties (Casamento & Niccol, 2023).
- Ketamine is associated with hallucinations, increased agitation, and delirium.
Neuromuscular Blockade
NMBAs, sometimes referred to as paralytics, paralyze skeletal muscles by blocking nerve impulse transmission. These medications are not to be used as initial management for agitation, undesired movement, or ventilator dyssynchrony (the timing of mechanical breaths is not in agreement with the patient's inspiratory attempts). These medications do not have analgesic or sedative properties, are not recommended first-line agents to control movement, and should only be used when the former mechanisms (e.g., sedation, analgesia) have failed. NMBAs should never be administered to a patient who does not have an advanced airway (e.g., intubated), as respiratory muscles will be paralyzed (Bittner, 2023). As discussed previously, NMBAs are also used for intubation following an induction sedative agent (Brown & Sackles, 2023). Additional circumstances in which NMBAs may be necessary include the following:
- Severe ventilator dyssynchrony unresolved with sedative or analgesic medications
- It may avert lung overinflation and injury by preventing the patient from "stacking" breaths on top of the ventilator's programmed respirations.
- It reduces oxygen consumption by the respiratory muscles and puts the work of breathing on the ventilator instead of the patient (Bittner, 2023).
- Severe shivering related to therapeutic hypothermia secondary to cardiac arrest
- Hypothermia prolongs the therapeutic duration of all nondepolarizing agents (Bittner, 2023).
- Protocols should be developed to guide the administration of NMBAs during therapeutic hypothermia (Renew et al., 2020).
- Preventing unwanted muscle movement when it may cause danger to the patient, such as when it contributes to elevated intracranial pressure or coughing that could dislodge a clot in the context of hemoptysis (Bittner, 2023)
Common intermediate-acting NMBAs include cisatracurium (Nimbex), vecuronium (Norcuron), and rocuronium (Zemuron). These medications may be given in bolus or continuous IV doses, but continuous infusions are generally preferred over bolus dosing. Weight-based dosing should be based on the patient’s ideal or adjusted body weight rather than their actual weight (Renew et al., 2020). Cisatracurium (Nimbex) is the preferred agent for continuous infusion because its metabolism is unrelated to hepatic or renal function. Atracurium is also a feasible option in patients with hepatic or renal insufficiency but should be avoided in hemodynamically unstable patients due to the potential for histamine release. A maintenance infusion of cisatracurium (Nimbex) is typically 1 to 3 mcg/kg/minute. Patients with severe sepsis/septic shock may have a delayed or diminished response to standard cisatracurium (Nimbex) dosing regimens, but there are no specific contraindications to its use. Neuromuscular blockade can be maintained using boluses of rocuronium (Zemuron) of 0.10 to 0.15 mg/kg (5 to 12 mcg/kg/minutes; Clar, 2023; Bittner, 2023). Patients may report pain on injection of rocuronium (Zemuron), and prolonged use in the ICU may lead to an extended half-life and a risk of myopathy, making it a less desirable choice and not commonly used. The maintenance dosing of vecuronium (Norcuron) is 0.1 mg/kg (1 to 2 mcg/kg/min). Both rocuronium (Zemuron) and vecuronium (Norcuron) can be reversed with sugammadex (Bridion; Bittner, 2023).
Titration of a continuous infusion of NBMA can be monitored with peripheral nerve stimulation (PNS), usually ulnar or facial, and measuring twitches of the impacted muscle. As the neuromuscular blockade progresses, fewer twitches will be produced with PNS (Renew, 2024). PNS should only be used in combination with clinical assessments and should not be used as a sole indicator of medication dosing or effectiveness. This combination can be used in patients undergoing therapeutic hypothermia (Renew et al., 2020). An alternative monitoring option is the Bispectral Index (BIS). A BIS monitor uses electrodes to analyze electroencephalogram (EEG) data and interpret a score from 0 to 100, with 0 indicating no brain activity and 100 representing full awareness. NMBAs may be titrated to BIS scores to determine whether a patient is adequately sedated. Tachycardia, tachypnea, and hypertension are potential indicators of patient awareness or agitation, but these are not validated measures and should not be used as the sole assessment tool (Renew, 2024).
Continuous NMBA infusion is typically avoided in status asthmaticus (Renew et al., 2020). Patients receiving NMBAs are also at elevated risk of multiple complications related to the complete cessation of muscle movement. When NMBAs are used for an extended period, the risk of muscle atrophy, foot drop, deep vein thrombosis (DVT), and pressure injury increases. Therapeutic range of motion should be performed every 4 hours, patients should be turned every 2 hours, and prophylactic anticoagulation medications should be ordered according to current industry guidelines (Blauvelt et al., 2019). Regularly scheduled eye care with lubrication drops/gel and eyelid closure is recommended for all patients on continuous neuromuscular blockade, and a target blood glucose of less than 180 mg/dL was a weak recommendation (Renew et al., 2020).
Patients receiving NMBAs may experience complications related to specific comorbidities. Blauvelt and colleagues (2019) outline the following considerations for interprofessional teams when patients are being administered NMBAs:
- Patients with a history of coronary artery disease are at increased risk of myocardial infarction due to vagolytic actions (reduced impulses from the vagus nerve, increased HR and cardiac output) of some NMBAs, especially pancuronium (Pavulon).
- Patients with hepatic or renal failure are at greater risk of prolonged effects of NMBAs since they are eliminated through the liver and kidneys, except atracurium (Tracrium) and cisatracurium (Nimbex).
- Rapid infusion of NMBAs may lead to a profound histamine release, causing hypotension, flushing, bronchospasm, and increased salivation, especially atracurium (Tracrium) and, to a lesser degree, cisatracurium (Nimbex) at very high doses.
Sedation Scales
Evidence regarding sedative and analgesic medications in the ICU demonstrates that proper titration using goal-directed therapy can optimize patient comfort and avoid complications such as reintubation or PMV rather than prioritizing which medication is administered. When sedatives are administered, goal-directed delivery is critical to prompt ventilator weaning. When interprofessional teams agree upon a targeted sedation level, the patient's risk for complications and recovery obstacles decreases (Wesley et al., 2003). Goal-directed sedation is often driven by using a validated sedation scale.
An interprofessional approach with sedation goals ensures that all care team members are on the same page, improving recovery times. Providing specific goals dictating the titration of sedative medications can be beneficial in the ICU. It has been supported that the use of lighter sedation results in sooner liberation from the ventilator and discharge from the ICU (Stollings et al., 2022). When sedative-analgesic protocols are in place and sedation-minimizing strategies are employed sedative and opioid doses are reduced overall. In addition, trials comparing continuous sedation with daily interruption of sedation demonstrated that patients receiving a daily interruption of sedative medications spent less time in the ICU and mechanically ventilated (Olsen et al., 2020). Protocolized sedation interruptions instead of assessment-driven sedation reduce the harmful effects of excessive sedation (Stollings et al., 2022).
By verifying the Richmond Agitation-Sedation Scale's (RASS) validity, Wesley and colleagues (2003) determined that objective and goal-directed sedation therapy in ICU patients is the recommended standard to avoid oversedation and promote early extubation. They also reinforced that interprofessional agreement for target levels of sedation allows the swiftest course of recovery. Sedation scales allow the staff to assess the patient and determine an objective measurement of sedation level to guide the titration of medications according to the patient's conditions and goal-directed therapy (Sessler et al., 2002).
The most used sedation scales are the RASS and the Riker Sedation-Agitation Score (SAS), both equally effective in their guidance of patient sedation levels (Sessler et al., 2002). The RASS values range across ten variables from +4 to -5, with specific assessment guidelines for the evaluator scoring the patient. The expanded scale designates values for patients' responses to physical versus verbal responses and assists the clinical team in titrating medications appropriately (Wesley et al., 2003).
RASS
Sessler and colleagues (2002) designed the RASS and presented the scoring criteria as follows.
- 4 - Combative
- Overtly combative or violent; immediate danger to staff
- 3 - Very Agitated
- Pulls on or removes tube(s) or catheter(s) or has aggressive behavior
- 2 - Agitated
- Frequent non-purposeful movement or patient-ventilator dyssynchrony
- 1 - Restless
- Anxious or apprehensive but movements not aggressive or vigorous
- 0 - Alert and Calm
- -1 - Drowsy
- Not fully alert but has sustained (more than 10 seconds) awakening, with eye contact, to voice
- -2 - Light Sedation
- Briefly (less than 10 seconds) awakens with eye contact to voice
- -3 – Moderate Sedation
- Any movement (but no eye contact) to voice
- -4 – Deep Sedation
- No response to voice, but any movement to physical stimulation
- -5 – Unarousable
- No response to voice or physical stimulation (Sessler et al., 2002)
SAS
The Riker SAS offers seven scoring points at which to categorize the patient's level of sedation. The SAS scoring criteria are outlined by Riker and colleagues (1999) as follows.
- 7 - Dangerous Agitation
- Pulling at ETT, trying to remove catheters, climbing over bedrails, striking at staff, thrashing side-to-side
- 6 – Very Agitated
- Requiring restraint and frequent verbal reminding of limits, biting ETT
- 5 – Agitated
- Anxious or physically agitated, calms to verbal instructions
- 4 – Calm and Cooperative
- Calm, easily arousable, follows commands
- 3 – Sedated
- Difficult to arouse but awakens to verbal stimuli or gentle shaking, follows simple commands but drifts off again
- 2 – Very Sedated
- Arouses to physical stimuli but does not communicate or follow commands, may move spontaneously
- 1 – Unarousable
- Minimal or no response to noxious stimuli, does not communicate or follow commands (Riker et al., 1999)
These scales help quantify the patient's sedation level, allowing for clear directives in managing ICU sedation and sedative medication titration. Evidence shows that for most patients in the ICU who are mechanically ventilated, an acceptable target score is 3 to 4 on the Riker SAS and -1 to 0 on the RASS (Fuchs & Bellamy, 2024).
Nursing Alert: Unplanned extubation is prevalent in patients who are agitated or undersedated, usually because they remove the ETT themselves. Patients who self-extubate should be monitored closely, with a low threshold for reintubation. The APRN should notify the provider immediately of self-extubation, as many of these patients require reintubation (Hyzy, 2024).
Many institutional protocols will also dictate a scheduled sedation interruption, barring any contraindications. During the sedative interruption, or while patients are minimally sedated, they should be able to follow simple commands such as squeezing the examiner's hand or sticking out their tongue (Olsen et al., 2020). Some patients, however, may have indications for continuous deep sedation (e.g., those with status epilepticus, elevated intracranial pressure, or the use of NMBAs). In such patients, underlying medical conditions must improve before sedation can be weaned or interrupted, allowing ventilator weaning to progress (Epstein, 2024a). Patients' sedation levels should be assessed continuously, and sedative medications should be titrated to a score agreed upon by the interprofessional team (Epstein & Walkey, 2024). Oversedation will likely prolong MV and produce poorer patient outcomes through the weaning process (Stollings et al., 2022).
Case Study 3
The APRN is caring for a patient who is ventilated and sedated with propofol (Diprivan) and fentanyl (Sublimaze). Their current RASS goal is -2 to 0. When the bedside nurse completes a neurological assessment, they say the patient's name and ask them to open their eyes. The patient stirs in the bed, shakes their head in response, and briefly opens their eyes. They do not look directly at the nurse or make eye contact.
1. What is this patient's RASS score, and is it appropriate given the ordered goal?
2. Are any adjustments to the sedative infusion needed?
Since the patient aroused to voice, but did not make or sustain eye contact, their RASS score is currently a -3. This means that they are more sedated than their goal of -2 to 0. Therefore, the sedative infusion should be reduced, titrating down until the patient becomes more alert and is able to sustain eye contact.
The Process of Weaning
Weaning is the process of reducing ventilator support, allowing patients to increase their work of breathing as they move toward independent ventilation (Epstein, 2024a). Weaning assesses the patient's ability to assume an increased proportion of their ventilation to determine if MV can be discontinued with positive outcomes. Weaning, like sedation, should also be approached with protocols, often driven by nursing and respiratory therapy staff. This entails a daily assessment of readiness to wean and a weaning trial if the patient passes a readiness assessment. Weaning protocols have been shown to reduce the duration of MV by up to 26% and reduce the length of stay in the ICU. Some facilities use computer-driven automated protocols, but most will apply manual protocols, meaning that healthcare staff will alter ventilator settings as the patient is weaned. Manual protocols can be tailored to the patient, providing an advantage of patient-centered care (Epstein & Walkey, 2024).
The early stages of weaning typically involve a gradual reduction in ventilator support, reducing individual settings such as PEEP and FiO2 on the ventilator, and checking patient tolerance. Vital signs and ABG values should be monitored per unit protocol to assess the patient's response to the changes in ventilator settings (Epstein, 2023). As a patient stabilizes, tolerates lower ventilator support, and passes readiness testing criteria, a spontaneous breathing trial (SBT) may be initiated to wean the patient from the ventilator more aggressively. SBTs may be carried out daily until a patient successfully demonstrates that they can independently support the work of breathing (Epstein & Walkey, 2024).
Readiness Testing
Before a patient can be weaned to less aggressive ventilator settings, it is crucial to determine that the patient is clinically ready to begin this process. Readiness testing evaluates if the patient is clinically suitable for decreased ventilator support; this should be completed by the patient's interprofessional care team to determine that weaning is appropriate (Epstein, 2024b). Premature weaning can lead to cardiovascular dysfunction, psychological distress, or respiratory muscle fatigue. To determine that a patient is ready to wean, Epstein and Walkey (2024) describe the following criteria that should be met based on the evidence-based guidelines published by the American College of Chest Physicians, American College of Critical Care Medicine, and American Association for Respiratory Care (Ouelette et al., 2017):
- The cause of respiratory failure has improved or resolved.
- The ABGs reflect sufficient oxygenation (i.e., a PaO2/FiO2 of at least 150 [or 120 in patients with a history of chronic hypoxemia] or Sp2 greater than 90%) on an FiO2 of 40% or less and PEEP of 5 or less on the ventilator.
- The ABG values indicate a pH above 7.25.
- The vital signs reflect that the patient is hemodynamically stable, with minimal or no use of vasopressors.
- The patient proves that they can initiate inspiratory effort, whether during sedation interruption or while lightly sedated.
Ideally, the patient should be arousable and able to follow simple commands. Additional criteria included in readiness testing include a hemoglobin level of at least 7 mg/dL and a core temperature of less than 38.5° C (101° F; Epstein, 2024a; Epstein & Walkey, 2024).
Spontaneous Breathing Trials (SBTs)
Studies analyzing SBTs compared to gradual weaning show conflicting data on which strategy produces a lessened MV time, making contrasting recommendations. However, research consistently suggests that SBTs are successful, efficient, and safe in most patients, making them an ideal method for ventilator weaning. A recent international study involving 1,868 adults mechanically ventilated for longer than 24 hours in six geographic regions globally found significant variation in weaning practices. Within this trial, direct extubation was related to a lower mortality rate and shorter duration of ventilation and ICU admission when compared with those undergoing a spontaneous breathing trial (SBT). However, the authors admit that this may be due to greater illness severity among those undergoing SBT. Findings indicate the need to further study optimal weaning practices worldwide (Burns et al., 2021; Epstein & Walkey, 2024).
When an SBT is initiated, the patient is switched from full respiratory support modes (consider the section on modes of ventilation - full support may be set volumes, RRs, or pressure support) to modes where the patient has more control of their ventilation, such as low-level PSV, automatic tube compensation, or CPAP. The use of PSV mitigates the increased work related to the presence of the ETT and is especially vital in those with an ETT size of seven or smaller. While the specifics vary by institution/clinician, generally, this can be achieved with inspiratory pressure augmentation of 5 to 8 centimeters H2O, a PEEP of 5 centimeters H2O, and an FiO2 of 40% or lower. These are consistent with the most recent national practice guidelines (Ouelette et al., 2017). Ventilatory support prevents the fatigue that may cause the patient to fail the SBT, and several clinical trials have shown that using the PSV mode is associated with higher success rates (i.e., extubation) when compared to other methods. Ideally, this should be done while the patient is awake and receiving little to no sedative medication (Epstein & Walkey, 2024).
Patient vital signs should be monitored during a weaning trial, including RR and TV. Alert patients should be asked about the presence of dyspnea or chest pain, and all patients should be observed for indications of respiratory distress and mental status changes. Telemetry monitors should be followed closely for ST changes, prompting electrocardiography to further assess cardiac ischemia (Epstein and Walkey, 2024). The criteria for a successful SBT are described by Epstein and Walkey (2024) as follows:
- The patient should breathe for 30 to 120 minutes with little to no ventilator support.
- The patient should not breathe faster than 35 breaths/minute for more than 5 minutes.
- The patient's oxygen saturation should not fall below 90% (or PaO2 50 mm Hg)
- The patient's heart rate should not increase greater than 140/min or sustain an increase greater than 20% from baseline.
- The patient's systolic blood pressure should remain between 90 to 180 mm Hg.
- The patient should not demonstrate a change in mental status (somnolence, delirium, or agitation), increased anxiety, diaphoresis, or indications of severe discomfort.
- The patient's heart rate should not fall below 50/min.
- The patient should not show signs of respiratory distress (e.g., accessory muscle use, thoracoabdominal paradox [the inward/upward movement of the abdomen] during inspiration, asynchronous with the chest rise, indicative of absent or unexpected diaphragmatic motion).
- The patient's PaCO2 should not increase greater than 10 mm Hg, and their pH should not decrease greater than 0.1 from the pre-weaning baseline.
Epstein and Walkey (2024) point out that for patients who have been mechanically ventilated for longer than ten days, extended SBTs of up to 2 hours are recommended. Some studies have demonstrated that patients with severe underlying respiratory illness could take over 2 hours to fail an SBT. Blood gas analysis may be completed after an SBT, especially in those patients at increased risk of hypercapnia (e.g., history of COPD; Epstein & Walkey, 2024). The patient's posture during the SBT should be individualized and according to their comfort. Patients with diaphragmatic paralysis typically prefer to be seated upright. Those with intercostal muscle weakness due to a lower cervical cord lesion may choose to be supine, while patients with COPD are more variable. The patient's airway should be suctioned entirely before each SBT to ensure no excess secretions are present. Short-acting inhaled bronchodilators (e.g., beta-adrenergic or anticholinergic agents) may be given before an SBT to reduce airway obstruction unrelated to the artificial airway (Epstein, 2024a). If a patient completes a successful SBT, extubation will be considered (Ouellette et al., 2017).
Patients who do not meet one or more of the SBT criteria may need to be placed back on ventilator support and repeat an SBT later (Ouellette, 2017). Patients who fail an SBT should resume their prior ventilator settings, which will allow them another 24 hours to recover from any fatigue before re-attempting another SBT (Epstein & Walkey, 2024). If a patient fails their SBT, the interprofessional team should be prompted to evaluate the patient's clinical picture to find possible causes, such as fluid status, pain control, bronchodilation requirement, or other potential reasons for continued respiratory distress. The ability to identify and treat a root cause of SBT failure may promote the patient's chances of passing in the future (Ouellette et al., 2017).
Alternative Methods
Although less common, alternatives to SBT are used infrequently. Pressure support weaning is performed by establishing a PEEP of 4 to 5 centimeters H2O and pressure support of 12 to 18 centimeters H2O, targeting 25 spontaneous respirations per minute. When able, the PSV is then reduced by 2 to 4 centimeters H2O twice daily. The final goal is for the patient to tolerate 5 to 8 centimeters H2O of pressure support for at least 2 hours. Protocols describing more rapid reduction schedules have also been described. While PSV weaning protocols have been shown to reduce ventilation duration compared to weaning at the discretion of the attending clinician, the data comparing PSV weaning to daily SBT are conflicting (Epstein & Walkey, 2024).
Intermittent mandatory ventilation weaning uses the IMV settings described above to establish a minimum RR and TV while allowing the patient to generate spontaneous breaths at will. These weaning protocols typically include starting the patient with an IMV of 8 to 12 and reducing the rate by 2 to 4 breaths/minute twice a day. The goal is for the patient to tolerate a rate of 4 to 5 breaths/minute (or less) for 2 hours or more. While IMV weaning protocols appear to reduce ventilation duration compared to weaning at the discretion of the attending clinician in clinical trials, they are not superior to daily SBTs and could be inferior (Epstein & Walkey, 2024). Finally, the use of noninvasive ventilation immediately following extubation has been proposed in patients who fulfill the initial readiness testing criteria but fail their SBT. This strategy has been used predominantly in patients with a history of COPD or chronic hypercapnic respiratory failure or those at high risk of extubation failure (Epstein & Walkey, 2024).
Barriers to Weaning
Some patients may struggle to complete an SBT for various reasons, which can be simple (e.g., oversedation) or complex (e.g., the long-term effects of chronic illness). Root causes must be identified, treated, and reassessed. Interprofessional teams should be in the habit of monitoring for pH overcorrection, pleural effusions, heart failure, pulmonary edema, cardiac ischemia, and patient stress related to breathing through the narrowed diameter of an ETT. Some patients struggle to breathe spontaneously with several failed trials; those who fail their first two SBTs are considered difficult to wean. If the process requires more than three attempts and more than a week, this is termed prolonged weaning. If a patient cannot pass an SBT after 7 to 14 days, placement of a tracheostomy should be considered (Epstein, 2024a; Epstein & Walkey, 2024).
Moving Toward Extubation
Once a patient demonstrates success in an SBT, careful consideration must be made to ensure that the patient is ready for extubation. Before removing an ETT, the APRN should evaluate the patient's ability to protect their airway and ensure airway patency once the advanced airway is removed. If the patient has a weak cough, excessive secretions, or poor mentation, the patient may be prone to aspiration once extubated. The inability to clear secretions due to an ineffective cough increases the risk that the patient will not tolerate extubation; this risk increases to 100% when a weak cough is combined with increased sputum volume and decreased level of consciousness. Obesity may also inhibit a patient's ability to protect their airway (Hyzy, 2024). When assessing a patient's readiness for extubation, the APRN should consider the following.
- Assessment of secretions should be completed. If a patient requires frequent suctioning (more than every 2 to 3 hours), has copious secretions (the volume can be measured using the suction canister), or if the secretions are excessively thick or dry, the medical team should consider delaying extubation (Epstein, 2024a, Hyzy, 2024).
- The patient should be assessed for a productive cough and the ability to clear secretions. If the patient can cough secretions through the ETT, they are more likely to clear secretions when extubated (Epstein, 2024). The cough can be assessed informally during deep ETT suctioning, using spirometry, or using an index card test (an index card is held 1 to 2 centimeters from the loose end of the ETT while the patient is instructed to cough three to four times). A patient who cannot moisten the index card is three times more likely to struggle with extubation than a patient who can (Hyzy, 2024).
- The patient's mental status directly impacts their ability to protect their airway. Studies show that patients with a GCS of 8 or above are more likely to be extubated successfully. The inability to perform simple commands is also associated with unsuccessful extubation (Epstein, 2024a; Hyzy, 2024).
Airway patency is paramount to the success of extubation. Airway patency should be assessed to identify patients who may be at risk for post-extubation stridor. Patients who had traumatic intubation, a large ETT (greater than 8 mm in men, 7 mm in women, a small ratio of patient height to ETT diameter, or greater than 45% ratio of ETT to laryngeal diameter on advanced imaging), prolonged intubation (this varies from greater than 36 hours to greater than 6 days), or advanced age (over 80 years) are at the highest risk. Other risk factors include an elevated APACHE II score, a GCS less than 8, female sex, a history of asthma, excessive tube mobility (i.e., insufficient fixation), deficient sedation, and the presence of aspiration. This can be assessed using a "cuff leak" test, in which the cuff around the ETT is deflated. If air does not pass (leak) around the ETT when the cuff is deflated, the patient is at higher risk for post-extubation stridor due to the reduced area between the ETT and the larynx. A cuff leak test is performed by auscultating for an air leak with a stethoscope placed over the superior trachea. Cuff leaks can also be assessed during volume-cycled ventilation by comparing the inspired and expired TV to establish the cuff leak volume. In this case, a cuff leak volume of at least 110 mL or 25% of the delivered TV is encouraging, while smaller volumes indicate an increased risk for stridor post-extubation (Epstein, 2024a; Hyzy, 2024).
In patients without risk factors for stridor, a cuff leak test is probably not necessary. In at-risk patients, failing the cuff leak test should indicate the need to delay extubation due to the potential for laryngeal edema. A short course of glucocorticoid may be administered before extubation to help reduce the swelling. Methylprednisolone (Medrol) 20 mg may be given every 4 hours for a total of 4 doses, or a single 40 mg dose may be administered approximately 4 hours before extubation (Hyzy, 2024).
Extubation
Extubation should be carried out only when there is adequate staffing and resources available to address the possibility of reintubation, which is most often during the day. Nighttime extubations (after 1900 hours) are rare. Those with a prior history of challenging intubation are assumed to be at high risk for difficulty while reintubating as well, and this should be considered when ensuring that staff and supplies are present if needed. Other factors to consider when timing extubation are the fatigue and availability of experts required to assist in the case of a problematic reintubation (Hyzy, 2024). While protocols will differ between institutions, the following are general guidelines for extubation (Epstein & Wakey, 2024; Hyzy, 2024).
- Tube feeds, if applicable, should be paused for at least an hour before extubation. Some facilities may measure residual volumes or aspirate gastric contents before extubation.
- Suction equipment (both oral and ETT) should be ready at the bedside to suction properly before extubation and manage oral secretions after the patient is extubated.
- A stethoscope should be present at the bedside to assess for post-extubation stridor.
- Suitable (i.e., according to the patient's condition) supplemental oxygen equipment should be ready at the bedside, such as a low-flow and high-flow nasal cannula, a face mask, or noninvasive ventilation equipment.
- Vital signs, including heart rate, respiratory rate, blood pressure, and SpO2, should be monitored closely during and after extubation.
- The patient should be sitting up as much as possible to promote airway clearance.
Other required equipment includes scissors (to cut/remove securement devices/tape) and a 10-cc syringe. Prior to extubation, the ETT and the patient's mouth should both be suctioned to ensure no secretions have pooled above the ETT cuff. To extubate, the ETT securement device is released by one team member while the ETT is held in place by another. The 10-cc syringe is attached for cuff deflation. The patient is instructed to cough or exhale, during which the cuff is quickly deflated, and the ETT is removed in a smooth, swift motion. Any orogastric tubes can be removed simultaneously with the ETT. Oral secretions should be suctioned to avoid aspiration. The APRN and providers should immediately auscultate for post-intubation stridor. A patient who develops stridor may have upper airway edema and may need to be reintubated (typically with a smaller ETT) and often given a short course of glucocorticoids, as described above. Patients at low risk for reintubation should be extubated with a regular nasal cannula at the bedside and weaned from this as tolerated (Epstein, 2024b; Hyzy, 2024).
Individualized plans for patients ensure that interventions are tailored to the patient's needs. Patient assessment is key in post-extubation care. When developing a plan of care for the patient following extubation, the interprofessional team should consider the O2 and PEEP requirements as well as respiratory drive while the patient is ventilated. Many patients tolerate eating within a few hours of extubation, especially those intubated for a week or less. Those who were intubated for longer than 2 weeks or those with confounding factors that increase their risk of aspiration (e.g., neuromuscular condition, decreased level of consciousness, critical care myopathy) may need to wait 12 to 24 hours before eating. A swallow evaluation completed by a speech and language pathologist is a more conservative option for allowing an at-risk patient to resume eating safely while minimizing the risk of aspiration. Patients may be considered for discharge from the ICU after 12 to 24 hours (Hyzy, 2024).
Some patients will assume the work of breathing appropriately after extubation but require additional O2 support. Risk factors for post-extubation respiratory failure include previously failed SBTs/extubations, a weak cough or absent cuff leak, a need for frequent suctioning (every 1 to 2 hours), GCS less than 8 or other altered mental status (e.g., delirium), a positive fluid balance in the 24 hours prior to extubation, age over 65 with a chronic cardiac or respiratory disease (e.g., heart failure, COPD), pneumonia as the primary indication for MV, pulmonary hypertension, interstitial lung disease, or multiple comorbidities. Following extubation, respiratory distress is typically related to poor secretion clearance, laryngeal edema, heart failure, bronchospasm, or aspiration. Respiratory failure following extubation typically presents with decreasing SpO2, increasing RR, stridor, and other indications of respiratory distress (e.g., accessory muscle use). A humidified high-flow nasal cannula (HFNC) provides O2 and PEEP support and has been shown to improve airway clearance and prevent reintubation in these patients. In combination with vigilant monitoring, preemptive NIPPV or HFNC are feasible options for extubated patients at increased risk for post-extubation respiratory failure. NIPPV is not used routinely for all patients following extubation but may be especially beneficial in those prone to hypercapnic respiratory failure (e.g., COPD) and those with heart failure. If a patient is stable but appears to be showing signs of respiratory distress following extubation, a blood gas analysis and a chest x-ray may be considered to help determine the underlying etiology of the dysfunction (Epstein, 2024a; Hyzy, 2024).
Unplanned extubations are not frequent, occurring in only 3% to 12% of intubated patients. The risk increases in patients with poorly secured ETTs, who are orally intubated (versus nasally), are agitated, less sedated, or physically restrained. The patient should be assessed promptly, and a low threshold should be set for immediate reintubation at the first indication of respiratory failure. Approximately half of the patients with unplanned extubations require reintubation within 12 hours (Hyzy, 2024).
In patients reintubated due to stridor, the cuff leak test should be repeated after a short course of glucocorticoids as previously described. If the patient passes this test, bedside extubation can be re-attempted. If the patient does not pass this secondary cuff leak test, an alternative is to extubate the patient over an airway exchange catheter (e.g., a Cook catheter), allowing for a quick and easy reintubation, if necessary (Hyzy, 2024).
If patients become tachypneic or show any manifestations of respiratory distress following extubation while on NIPPV, reintubation may be necessary. The underlying cause of respiratory failure should be identified to avoid future difficulty with subsequent extubation attempts. These are most often cardiac or respiratory but may be psychological (anxiety, depression, delirium), ventilator, or nutrition-related. The assessment should include a clinical exam (to identify laryngeal edema or heart failure), laboratory studies (i.e., complete blood count, electrolyte/metabolic panel, blood gas analysis), electrocardiography (to identify arrhythmias, heart failure, myocardial ischemia), and a chest x-ray (to determine aspiration, heart failure, pleural effusion). The ventilator circuit should be evaluated (assessing for auto-PEEP or overventilation), as well as the patient's current sedative/analgesic medications. MV should be continued for an additional 1 to 2 days before attempting to extubate again while the underlying cause is addressed (e.g., diuretics to manage heart failure, sedative medication adjustments to optimize the level of consciousness, along with any mood disorder manifestations). A patient who fails more than one extubation trial generally requires a tracheostomy for extended weaning protocols (Epstein, 2024a; Hyzy, 2024). As mentioned earlier, tracheostomy placement enhances patient comfort, reduces the need for sedation, and facilitates weaning (Hyzy & McSparron, 2024).
Long-term acute care (LTAC) facilities focus solely on rehabilitation and ventilator weaning in challenging patients. Patients who may benefit from a transfer to such a facility include those with difficulty weaning previously, no ongoing acute illness, no dyspnea or hypoxemia during ventilation, a stable airway (e.g., tracheostomy), and a reliable route for daily nutrition in place (e.g., enteral feeding tube). These programs incorporate many of the tenets of rehabilitation nursing with respiratory care, integrating the family, caregivers, and exercise to accomplish specified and focused weaning goals (Epstein, 2024a).
Case Study 4
The APRN is working with the respiratory therapist to conduct an SBT for a patient. The sedation infusions have been paused to ensure the patient remains awake and alert, and the ventilator has been set to PSV. This patient has a history of two failed SBTs, and this is the third attempt in as many days. The respiratory therapist places the patient on an FiO2 of 30%. The APRN notices that as the patient becomes more alert, they are coughing and clearing their secretions through the ETT. The APRN asks the patient if they can hear them, and the patient nods their head yes. The APRN asks the patient to squeeze their hand, which they do, and also stick out their tongue when asked. The APRN continues to monitor the vital signs and mental status, which remain stable and consistent. The patient is not on any vasopressors. The patient's lung sounds are clear, their RR is stable, and they are using no accessory muscles to breathe. After 30 minutes, the patient remains stable.
Should the APRN continue the SBT, or begin moving toward extubation?
Should the APRN check the patient for the risk of post-extubation stridor, and if so, how will they do this?
If the patient is ready to extubate, what equipment should be at the bedside in preparation?
Considerations: This patient has had two failed SBTs in the past, so they are at a higher risk of extubation.
The patient is alert, calm, and following commands. Their respiratory status and vital signs appear stable, and the ventilator settings are suitable for extubation. Since they have had failed SBTs in the past, it may be appropriate to extend this SBT beyond 30 minutes.
To check for the risk of stridor, the APRN will deflate the cuff of the ETT. If air does not escape around the cuff, there is an increased risk of post-extubation stridor.
To extubate, the APRN should ensure a 10-cc syringe, suction equipment, and supplemental O₂ equipment are at the bedside. They should suction the patient’s mouth before the cuff is deflated and ETT removed and auscultate the patient's lungs and trachea upon extubation.
Due to the prior failed SBTs, the interprofessional team may want to have NIPPV equipment at the bedside as an additional precaution.
References
Achanti, A. & Szerlip, H. M. (2023). Acid-base disorders in the critically ill patient. Clinical Journal of the American Society of Nephrology, 18(1), 102–112. https://doi.org/10.2215/CJN.04500422
Ahmed, R. A. & Boyer, T. J. (2023) Endotracheal tube. StatPearls [Internet]. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK539747
Allen, G. B. (2023). Invasive mechanical ventilation in acute respiratory failure complicating chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. UpToDate. Retrieved March 19, 2024, from https://www.uptodate.com/contents/invasive-mechanical-ventilation-in-acute-respiratory-failure-complicating-chronic-obstructive-pulmonary-disease
Bittner, E. A. (2023). Neuromuscular blocking agents in critically ill patients: Use, agent selection, administration, and adverse effects. UpToDate. Retrieved March 29, 2024, from https://www.uptodate.com/contents/neuromuscular-blocking-agents-in-critically-ill-patients-use-agent-selection-administration-and-adverse-effects
Blauvelt, G., Burdick, K., & Cannon, E. J. (2019). Nursing considerations when using neuromuscular blocking agents to assist with intubation. Critical Care Nursing Quarterly (42)1, 30–40. https://doi.org/10.1097/CNQ.0000000000000234
Brown, C. A. (2023). The decision to intubate. UpToDate. Retrieved March 26, 2024, from https://www.uptodate.com/contents/the-decision-to-intubate
Brown, C. A. & Sakles, J. C. (2023). Rapid sequence intubation in adults for emergency medicine and critical care. UpToDate. Retrieved March 18, 2024, from https://www.uptodate.com/contents/rapid-sequence-intubation-in-adults-for-emergency-medicine-and-critical-care
Burns, K., Rizvi, L., Cook, D. J., Lebovic, G., Dodek, P., Villar, J., Slutsky, A. S., Jones, A., Kapadia, F. N., Gattas, D. J., Epstein, S. K., Pelosi, P., Kefala, K., Meade, M. O., & Canadian Critical Care Trials Group. (2021). Ventilator weaning and discontinuation practices for critically ill patients. Journal of the American Medical Association, 325(12), 1173–1184. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2021.2384
Casamento, A. & Niccol, T. (2023). Efficacy and safety of ketamine in mechanically ventilated intensive care unit patients: A scoping review. Critical Care and Resuscitation: Journal of the Australasian Academy of Critical Care Medicine, 24(1), 71–82. https://doi.org/10.51893/2022.1.OA9
Casamento, A., Serpa Neto, A., Young, M., Lawrence, M., Taplin, C., Eastwood, G. M., Ghosh, A., & Bellomo, R. (2021). A phase II cluster-crossover randomized trial of Fentanyl versus Morphine for analgosedation in mechanically ventilated patients. American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine, 204(11), 1286–1294. https://doi.org/10.1164/rccm.202106-1515oc
Castro, D., Patil, S. M., & Keenhagan, M. (2024). Arterial blood gas. StatPearls [Internet]. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK536919
Chanques, G. & Gélinas, C. (2022). Monitoring pain in the intensive care unit (ICU). Intensive Care Medicine, 48, 1508–1511. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00134-022-06807-w
Chrimes, N., Higgs, A., Hagberg, C. A., Baker, P. A., Cooper, R. M., Greif, R., Kovacs, G., Law, J. A., Marshall, S. D., Myatra, S. N., O'Sullivan, E. P., Rosenblatt, W. H., Ross, C. H., Sakles, J. C., Sorbello, M., & Cook, T. M. (2022). Preventing unrecognised oesophageal intubation: A consensus guideline from the Project for Universal Management of Airways and international Airway Societies. Anaesthesia, 77(12), 1395–1415. https://doi.org/10.1111/anae.15817
Clar, D. (2023). Non-depolarizing neuromuscular blockers. StatPearls. https://www.statpearls.com/ArticleLibrary/viewarticle/25811
Emmet, M. & Palmer, B. F. (2022). Simple and mixed acid-base disorders. UpToDate. Retrieved March 19, 2024, from https://www.uptodate.com/contents/simple-and-mixed-acid-base-disorders
Epstein, S. K. (2024a). Management of the difficult-to-liberate adult patient in the intensive care unit. UpToDate. Retrieved March 19, 2024, from https://www.uptodate.com/contents/management-of-the-difficult-to-liberate-adult-patient-in-the-intensive-care-unit
Epstein, S. K. (2024b). Weaning from mechanical ventilation: Readiness testing. UpToDate. Retrieved March 26, 2024, from https://www.uptodate.com/contents/weaning-from-mechanical-ventilation-readiness-testing
Epstein, S. K. & Walkey, A. (2024). Initial weaning strategy in mechanically ventilated adults. UpToDate. Retrieved March 22, 2024, from https://www.uptodate.com/contents/initial-weaning-strategy-in-mechanically-ventilated-adults
Flynn, G., & Shehabi, Y. (2012). Pro/con debate: Is etomidate safe in hemodynamically unstable critically ill patients? Critical Care, 16(4), 227. https://dx.doi.org/10.1186%2Fcc11242
Fuchs, B. (2024). Sedative-analgesia in ventilated adults: Medication properties, dosage regimens, and adverse effects. UpToDate. Retrieved March 27, 2024, from https://www.uptodate.com/contents/sedative-analgesia-in-ventilated-adults-medication-properties-dose-regimens-and-adverse-effects
Fuchs, B. & Bellamy, C. (2024). Sedative-analgesia in ventilated adults: Management strategies, agent selection, monitoring, and withdrawal. UpToDate. Retrieved March 24, 2024, from https://www.uptodate.com/contents/sedative-analgesia-in-ventilated-adults-management-strategies-agent-selection-monitoring-and-withdrawal
Hallett, S., Toro, F., & Ashurst, J. V. (2023). Physiology, tidal volume. StatPearls [Internet]. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK482502
Hyzy, R. C. (2023). Clinical and physiologic complications of mechanical ventilation: Overview. Retrieved March 26, 2024, from https://www.uptodate.com/contents/clinical-and-physiologic-complications-of-mechanical-ventilation-overview
Hyzy, R. C. (2024). Extubation management in the adult intensive care unit. UpToDate. Retrieved March 29, 2024, from https://www.uptodate.com/contents/extubation-management-in-the-adult-intensive-care-unit
Hyzy, R. C. & Jia, S. (2023). Modes of mechanical ventilation. UpToDate. Retrieved March 27, 2024, from https://www.uptodate.com/contents/modes-of-mechanical-ventilation
Hyzy, R. C. & McSparron, J. I. (2024). Tracheostomy: Rational, Indication, and Contradictions. UpToDate. Retrieved March 27, 2024, from https://www.uptodate.com/contents/tracheostomy-rationale-indications-and-contraindications
Lei, Y. (2017). Mechanical ventilator system basics: A clinical guide. https://doi.org/10.1093/med/9780198784975.001.0001
Lewandowska, K., Weisbrot, M., Cieloszyk, A., Mędrzycka-Dąbrowska, W., Krupa, S., & Ozga, D. (2020). Impact of alarm fatigue on the work of nurses in an intensive care environment—A systematic review. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 17(22), 8409. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17228409
Mora Carpio, A. L., & Mora, J. I. (2023). Ventilator management. StatPearls [Internet]. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28846232
Morelli, A., Sanfilippo, F., Arnemann, P., Hessler, M., Tim, G., D’Egidio, A., Orecchioni, A., Santonocito, C., Frati, G., Greco, E., Westphal, M., Rehberg, S., & Ertmer, C. (2019). The effect of propofol and dexmedetomidine sedation on norepinephrine requirements in septic shock patients: A crossover trial. Critical Care Medicine, 47(2), 89–95. https://doi.org/10.1097/CCM.0000000000003520
Murray, H., Grey, N., Wild, J., Warnock-Parkes, E., Kerr, A., Clark, D. M., & Ehlers, A. (2020). Cognitive therapy for post-traumatic stress disorder following critical illness and intensive care unit admission. The Cognitive Behaviour Therapist, 13, e13. https://doi.org/10.1017/S1754470X2000015X
Olsen, H. T., Nedergaard, H. K., Strøm, T., Oxlund, J., Wian, K., Ytrebø, L. M., Kroken, B. A., Chew, M., Kormaz, S., Lauridsen, J. T., & Toft, P. (2020). Nonsedation or light sedation in critically ill, mechanically ventilated patients. New England Journal of Medicine, 382(12), 1103–1111. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1906759
Ouellette, D. R., Patel, S., Girard, T. D., Morris, P. E., Schmidt, G. A., Truwit, J. D., Alhazzani, W., Burns, S. M., Epstein, S. K., Esteban, A., Fan, E., Ferrer, M., Fraser, G. L., Gong, M. N., Hough, C. L., Mehta, S., Nanchal, R., Pawlik, A. J., Schweickert, W. D., Sessler, C. N., Strøm, T., & Kress, J. P. (2017). Liberation from mechanical ventilation in critically ill adults: An official American College of Chest Physicians/American Thoracic Society clinical practice guideline: Inspiratory pressure augmentation during spontaneous breathing trials, protocols minimizing sedation, and noninvasive ventilation immediately after extubation, Chest, 151(1) 166–180. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chest.2016.10.036
Poncette, A., Mosch, L., Spies, C., Schmiding, M., Schifenhovel, F., Krampe, H., & Balzer, F. (2020). Improvements in patient monitoring in the intensive care unit: Survey study. Journal of Medical Internet Research, 22(6). https://doi.org/10.2196/19091
Reade, M. C., Eastwood, G. M., Bellomo, R., Bailey, M., Bersten, A., Cheung, B., Davies, A., Delaney, A., Ghosh, B., van Haren, F., Harley, N., Knight, D., McGuiness, S., Mulder, J., O'Donoghue, S., Simpson, N., & Young, P. (2016). Effect of dexmedetomidine added to standard care on ventilator-free time in patients with agitated delirium: A randomized clinical trial. Journal of the American Medical Association, 315(14), 1460–1468. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2016.2707
Reel, B. & Maani, C. V. (2023). Dexmedetomidine. StatPearls [Internet]. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30020675
Renew, J. R. (2024). Monitoring neuromuscular blockade. UpToDate. Retrieved March 21, 2024, from https://www.uptodate.com/contents/monitoring-neuromuscular-blockade
Renew, J. R., Ratzlaff, R., Hernandez-Torres, V., Brull, S. J., & Prielipp, R. C. (2020). Neuromuscular blockade management in the critically ill patient. Journal of Intensive Care, 8(37). https://doi.org/10.1186/s40560-020-00455-2
Riker, R. R., Picard, J. T., & Fraser, G. L. (1999). Prospective evaluation of the Sedation-Agitation Scale for adult critically ill patients. Critical Care Medicine, 27(7), 1325–1329. https://doi.org/10.1097/00003246-199907000-00022
Sessler, C. N., Gosnell, M. S., Grap, M. J., Brophy, G. M., O'Neal, P. V., Keane, K. A., Tesoro, E. P., & Elswick, R. K. (2002). The Richmond Agitation-Sedation Scale: Validity and reliability in adult intensive care patients. American Journal of Respiratory Critical Care Medicine, 166, 1338–1344. https://doi.org/10.1164/rccm.2107138
Stollings, J., Balas, M., & Chanques, G. (2022). Evolution of sedation management in the intensive care unit (ICU). Intensive Care Medicine, 48, 1625–1628. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00134-022-06806-x
Temesgen, N., Chekol, B., Tamirie, T. Eshetie, D., Simeneh, N., & Feleke, A. (2021)Adult sedation and analgesia in a resource-limited intensive care unit – A systematic review and evidence-based guideline. Annals of Medicine and Surgery, 66. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amsu.2021.102356
Theodore, A. C. (2023). Arterial blood gases. UpToDate. Retrieved March 19, 2024, from https://www.uptodate.com/contents/arterial-blood-gases
Wesley, E. W., Truman, B., Shintani, A., Thomason, J. W. W., Wheeler, A. P., Gordon, S., Francis, J., Speroff, T., Gautam, S., Margolin, R., Sessler, C. N., Dittus, R. S., & Bernard, G. R. (2003). Monitoring sedation status over time in ICU patients: Reliability and validity of the Richmond Agitation-Sedation Scale (RASS). Journal of the American Medical Association, 289(22), 2983–2991. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.289.22.2983